Note well: These manual pages have largely been superceded by new on-line "Help variables" and "How Do I" functions. These functions are available on line within the model page itself. [Tell me more]
The list below is provided as a convenience to users 1) who are accustomed to using it from past model versions or 2) who feel that they prefer to access a searchable, printable comprehensive list of how to manipulate the model. Users should realize that more functional information is available via the on-line links than exists in this list.
Artificial
Heart
HUMAN contains an artificial
heart that allows user control of the volume pumped per unit time
(within the limits set by venous return). Activating the artificial heart requires
setting at least one and at most 2 parameters. They are (consult
Help_variables or List of Variables )
Artificial respirator
HUMAN allows user control
of respiration volume and frequency. To set the respirator up
requires setting 3 parameters. They are (consult Help_variables
or List of Variables )
A common user error is set ARRT
& ARVOL but forget to throw the respirator switch on!
Exercise
Human allows control of the level of 'endurance' exercise through
the use of two user-selectable parameters. There are
Some additional useful variables/parameters when working in exercise include but are not limited to
02DEBT Muscle Oxygen Debt (0.0 ml)
FO2AT Fractional 02 in Atmosphere ( 0.21 ) - raising this to 1.0 allows administration of 100% O2.
FCO2AT Fractional C02 in Atmosphere (0.0)
LHSB Basic Left Heart Strength (1.0 X Normal) & RHSB Basic Right Heart Strength (1.0 X Normal)
- the combination of these heart strength controls allow for the simulation of cardiac endurance exercise conditioning (try 1.3 for each, a 30% stronger heart; see the effect on muscle O2 flow delivery). Remember to set BOTH sides upward and equally.
Infusions
HUMAN allows for the infusion of a user selectable volume, rate
and composition of infusate. Infusion involves setting at least
one parameter, the volume and up to six parameters totally. They
are (consult Help_variables or List
of Variables )
Infusions can be put to a wide variety of uses. Some examples follow
Pathology Inducers
Physiologically pathologic
states are normally induced in HUMAN by simply resetting parameters
to create the pathology and running the model for an amount of
time suitable to allowing the pathology to fully develop. Thus
changing TEMSET, the hypothalamic temperature set point, to 39
deg. C from its default value of 37 deg. C will induce a fever
state with all of its associated symptoms and problems. Prospective
pathology induction variables may be viewed by simply scanning the list of changeable
variables (parameters) for useful forcing variables.
HUMAN also contains certain specific parameters who sole
purpose is to induce a specific pathology. These, and some particularly
useful other inducers are listed immediately below.
ALDOP - induces primary aldosteronism on a user adjustable scale of severity from 0.0 to 10.0.
This simulates a a tumor of the zona glomerulosa of the adrenals that over secretes the mineralocorticoid, aldosterone (ALDO) with all of its sequella including hypertension, hypokalemia and Na+ retention plus extracellular fluid (ECFV) and blood volume (BV) expansion.AVFIST - induces an arterial -> venous fistula specified as a fraction of the total cardiac output (COL). Resulting values of fistula flow can be read out by the variable AVFLOW (ml/min.). A-V fistulas, direct communications between the arterial and venous circulation, provide a direct shunt pathway bypassing the vascular bed resistances. They thereby cause initial drops in total peripheral resistance (TPR) and concomitant initial decreases in arterial pressure (AP).
CAD - No Lipator®, balloon angioplasty or stents here but HUMAN can get coronary artery disease. Resetting CAD induces coronary artery disease of a severity varying between none (0.0, the default) to severe (=1.0) selectable by the user. Affects both coronary flow and cardiac function levels. Try nitroglycerine and vasodilators to relieve.
CLAMP - places a resistive clamp on the renal arteries whose effectiveness is measured in mmHg reduction of the arterial pressure perfusing the kidneys. Thus, with an arterial pressure (AP) of 100 mmHg, a renal artery CLAMP = 40 (mmHg) will reduce the pressure perfusing the kidneys (RENPP) to 60 mm Hg. This mimics sclerosis of the renal arteries (classic Goldblatt hypertension) and tends to initiate renally-induced systemic hypertension.
EXPRB - specifies basic protein loss via the kidney which has a normal value of 0.00035 gram/min.. Raising renal protein loss can be used to simulate aspects of glomerular nephritis and manipulate plasma osmolarity (POSM).
Hemorrhage - can be induced of a selectable volume and duration. The parameters to adjust follow.
- HEMVOL - specifies the total volume of the blood loss in ml..
- HEMMIN - specifies the timespan over which the hemorrhage of size HEMVOL takes place.
Thus, HEMVOL = 500 (ml.) and HEMMIN = 50 (min.) yields a 10 ml/min. blood loss that terminates at 50 min.. Replacement strategies should consider both volume and red cell replacement.
MSA - mean pulmonary surface area available for diffusion specified as a %-age. The default is 100 (%) and diffusion problems of varying severity can be simulated by reductions (MSA < 100%). Try MSA = 20 to simulate lung diffusive surface reductions such as in some types of severe emphysema and follow the effects on arterial oxygen (PO2A) over time.
Myocardial infarction(MI) - Yes, HUMAN can also have a heart attack! MI is inducible in HUMAN on either the left (LMIB) or the right (RMIB) side of the heart or bilaterally (set both LMIB & RMIB).
-The value selected indicates the fraction of cardiac function lost due to the infarct.
- Partial recovery of up to 30% can occur within several days.
- Be aware that response to MI may differ depending on the work levels placed on the heart.
PHEO - a pheochromocytoma, a tumor of the adrenal medulla that oversecretes adrenergic neurohumors, can be induced in HUMAN.
REMASS - Anatomical nephrectomy, the removal of a fraction of working kidney, can be studied by reducing the working renal mass from its normal full value (REMASS = 1.0) anywhere down to total nephrectomy (REMASS = 0.0). The later will yield full-blown classic uremic syndrome symptoms in HUMAN.
RENDIS - simulates renal disease as a reduction of functional renal mass ranging from none (RENDIS =0.0) to severe (RENDIS=4.0). Larger values of renal disease settings tend to induce a progressive deepening of its severity.
Finally, a reminder. The list
above is by no means exhaustive of the routes of inducing physiologic
pathology in HUMAN but rather covers only some of the more explicitly
pathologic inducers.
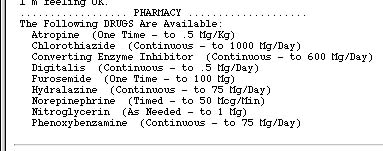
Pharmacy
This version of HUMAN
contains a limited pharmacy (but no co-pays!) the contents of
which (see below) can be viewed via selecting the <Patient Charts> option
and rolling down to the Pharmacy
choice.

Use of each drug is turned on via changing the variable corresponding to it via the <Change Variable> option from zero to the desired dosage. Note that doses are either one time or continuous as indicated.
A list of pharmacy drugs and some additional 'hidden' drugs follows.
I. Pharmacy drugs
II. Additional non-pharmacy
"drugs"
This version of HUMAN also contains several additional pharmaceutical-like
interventions, as a glance through the variables list reveals.
Some of these are noted below.
Transfusions
HUMAN allows for blood transfusions of a user selectable volume
delivered over a user selectable period of time. Transfusion
hematocrit can also be controlled. The three variables controlling
blood transfusion are
Transfusions offer a wide variety of possibilities. For example
Urine collection (24 hours or specimen)
A 24 urine collection can be initiated by setting the parameter switch U24 from its default value of 0.0 ( = No) to 1.0 ( = do it). This initiates the collection. Values generated by the collection can then be read out 24+ hours later.
- Under the Patient Charts option, roll down to select the option <24 hr Urine Collection> and values will be shown for the following:
24-Hour Urinary Potassium ( 42.0 mEq/L )
24-Hour Urinary Sodium ( 118.0 mEq/L )
24-Hour Urine Osmolarity ( 760.0 mOs/L )
24-Hour Urinary Protein ( 0.035 g/dl )
24-Hour Urine Volume ( 1440.0 ml )
An on-the-spot urine specimen can be initiated as
follows:
- Under the Patient Charts option, roll down to select the option <Urine Specimen > and values will be shown for the following:
Urine Potassium ( 42.0 mEq/L )
Urine Sodium ( 118. mEq/L )
Urine Osmolarity ( 760.0 mOs/L )
Urine pH (7.1 pH Units)
Urine Protein (0.035 g/dl)
(Average normal values are indicated
in parenthesis)
[ We would like to thank Dr. Coleman for generously releasing the HUMAN code for use in web-HUMAN and Dr. Randall for his kind words of encouragement ].
1) HUMAN - Physiological Basis of A Comprehensive Model For Body Function - 1981 Version. Thomas G. Coleman.
2) HUMAN - FORTRAN Source Code and Comments. Thomas Coleman - 1979 Version.
3) HUMAN - 80 - Microcomputer Version of A Mathematical Model ... (1981-7)
Instructor's Manual Thomas Coleman and James E. Randall
Physiological Basis of A Comprehensive Model For Body Function Thomas Coleman
Student's Manual Thomas Coleman and James E. Randall
.